Relations and Functions - Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Mathematics
Chapter-01
Relation and Function
TYPES OF RELATIONS:
- Empty Relation: It is the relation R in X given by R = .
- Universal Relation: It is the relation R in X given by R = .
- Reflexive Relation: A relation R in a set A is called reflexive if (a, a) ∈ R for every a ∈ A.
- Symmetric Relation: A relation R in a set A is called symmetric if (
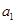 ,
, 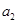 ) ∈ R implies that (
) ∈ R implies that (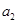 ,
, 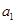 ) ∈ R, for all
) ∈ R, for all 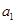 ,
, 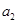 ∈
∈ - Transitive Relation: A relation R in a set A is called transitive if (
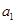 ,
, 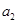 ) ∈ R, and (
) ∈ R, and (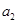 ,
, 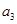 ) ∈ R together imply that all
) ∈ R together imply that all 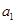 ,
, 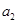 ,
, 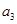 ∈ A.
∈ A. - EQUIVALENCE RELATION : A relation R in a set A is said to be an equivalence relation if R is reflexive, symmetric and transitive.
- Equivalence Classes: Every arbitrary equivalence relation R in a set X divides X into mutually disjoint subsets (Ai) called partitions or subdivisions of X satisfying the following conditions:
All elements of Ai are related to each other for all i.
No element of Ai is related to any element of Aj whenever i ≠ j 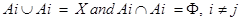
· . These subsets (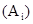 ) are called equivalence classes.
) are called equivalence classes.
· For an equivalence relation in a set X, the equivalence class containing a ∈ X, denoted by [a], is the subset of X containing all elements b related to a.
**Function: A relation f: A  B is said to be a function if every clement of A is correlated to a
B is said to be a function if every clement of A is correlated to a
Unique element in B.
*A is domain
* B is codomain
- A function : X Y is one-one (or injective), if .
- A function : X Y is onto (or surjective), if such that
- A function : X Y is one-one-onto (or bijective), if is both one-one and onto.
- The composition of function : A B and : B C is the function given by
- A function : X Y is invertible, if such that and
- A function : X Y is invertible, if and only if is one-one and onto.
- Given a finite set X, a function : X X is one-one (respectively onto) if and only if is onto (respectively one-one). This is the characteristics property of a finite set. This is not true for infinite set.
- A binary function * on A is a function * from A x A to A.
- An element is the identity element for binary operation * : , if
- An element is invertibel for binary operation * : if there exists such that where is the binary identity for the binary operation *. The element is called the inverse of and is denoted by .
- An operation * on X is commutative, if in X.
- An operation * on X is associative, if in X.