Application of Derivatives - Exemplar Solutions
CBSE Class–12 Mathematics
NCERT Exemplar
Chapter - 6
APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES - Short Answer Questions
1. For the curve  if
if 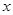 increases at the rate of 2 units/sec, then how fast is the slope of curve changing when
increases at the rate of 2 units/sec, then how fast is the slope of curve changing when 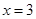 ?
?
Sol. To find slope of tangent to the given curve at different point, differentiate it w.r.t x
To find the rate of change of slope, differentiate the slope w.r.t. time(t)
Thus, slope of curve is decreasing at the rate of 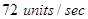 when
when 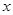 is increasing at the rate of
is increasing at the rate of 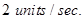
2. Water is dripping out from a conical funnel of semi-vertical angle  at the uniform rate of
at the uniform rate of 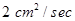 in the surface area, through a tiny hole at the vertex of the bottom. When the slant height of cone is 4 cm, find the rate of decrease of the slant height of water.
in the surface area, through a tiny hole at the vertex of the bottom. When the slant height of cone is 4 cm, find the rate of decrease of the slant height of water.

Sol.If s represents the surface area, then

Also, on using trigonometric ratios, radius of cone can be taken as

Therefore, 
when 
Thus, rate of decrease of slant height of water is
3. Find the angle of intersection of the curves 
Sol.Solving the given equations, we have 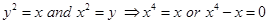
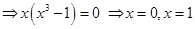
Therefore, 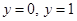
i.e. points of intersection are 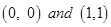
Further 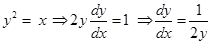
and 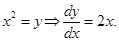
At  the slope of the tangent to the curve
the slope of the tangent to the curve 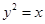 is parallel to y-axis and the tangent to the curve
is parallel to y-axis and the tangent to the curve  is parallel to x-axis.
is parallel to x-axis.
 angle of intersection
angle of intersection 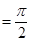
At (1, 1) slope of the tangent to the curve 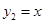 is equal to
is equal to 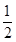 and that of
and that of  is 2.
is 2.
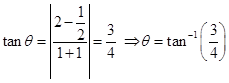
4. Prove that the function  is strictly decreasing on
is strictly decreasing on  .
.
Sol.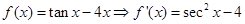
When
Therefore, 
Thus for 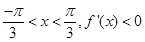
Hence 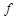 is strictly decreasing on
is strictly decreasing on  .
.
5. Determine for which values of x, the function 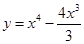 is increasing and for which values, it is decreasing.
is increasing and for which values, it is decreasing.
Sol.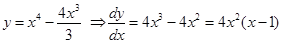
Now, 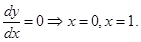
Since  and
and 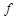 is continuous in
is continuous in 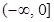 and [0, 1].
and [0, 1].
Therefore, 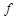 is decreasing in
is decreasing in 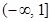 and
and 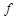 is increasing in
is increasing in 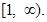
Note: Here 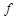 is strictly decreasing in
is strictly decreasing in  and is strictly increasing in
and is strictly increasing in  .
.
6. Show that the function 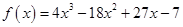 has neither maxima nor minima.
has neither maxima nor minima.
Sol.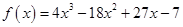
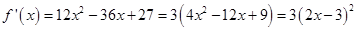

Since 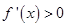 for all
for all 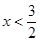 and for all
and for all 
Hence 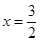 is a point of inflexion i.e., neither a point of maxima nor a point of minima.
is a point of inflexion i.e., neither a point of maxima nor a point of minima.
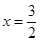 is the only critical point, and
is the only critical point, and 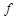 has neither maxima nor minima.
has neither maxima nor minima.
7. Using differentials, find the approximate value of 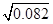
Sol.Let 
Using
we get

= 0.3 – 0.0133 = 0.2867.
8. Find the condition for the curves 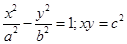 to intersect orthogonally.
to intersect orthogonally.
Sol.Let the curves intersect at 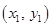 . Therefore,
. Therefore,
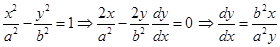
 slope of tangent at the point of intersection
slope of tangent at the point of intersection 
Again 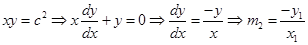 .
.
For orthoganality, 
9. Find all the point of local maxima and local minima of the function 
Sol.
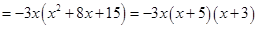

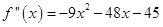

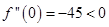 . Therefore,
. Therefore,  is point of local maxima
is point of local maxima
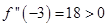 . Therefore,
. Therefore, 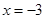 is point of local minima
is point of local minima
 . Therefore,
. Therefore,  is point of local maxima.
is point of local maxima.
10. Show that the local maximum value of 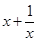 is less than local minimum value.
is less than local minimum value.
Sol.Let 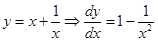
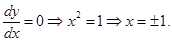
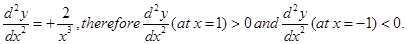
Hence local maximum value of 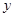 is at
is at  and the local maximum value
and the local maximum value 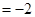 .
.
Local minimum value of 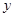 is at
is at  and local minimum value
and local minimum value 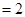 .
.
Therefore, local maximum value 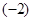 is less than local minimum value
is less than local minimum value  .
.
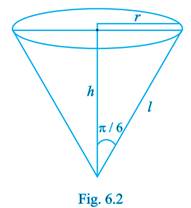
11. Water is dripping out at a steady rate of 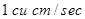 through a tiny hole at the vertex of the conical vessel, whose axis is vertical. When the slant height of water in the vessel is 4 cm, find the rate of decrease of slant height, where the vertical angle of the conical vessel is
through a tiny hole at the vertex of the conical vessel, whose axis is vertical. When the slant height of water in the vessel is 4 cm, find the rate of decrease of slant height, where the vertical angle of the conical vessel is 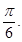
Sol.Given that  where
where  is the volume of water in the conical vessel.
is the volume of water in the conical vessel.
From the Fig.6.2, 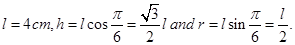
Therefore, 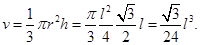
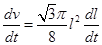
Therefore, Rate of decrease of slant height, when slant height is 4 units. 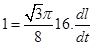
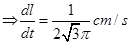
Therefore, the rate of decrease of slant height  .
.
12. Find the equation of all the tangents to the curve y = cos (x + y),  that are parallel to the line
that are parallel to the line 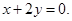
Sol.Given that 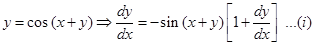

Since tangent is parallel to 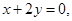 therefore slope of tangent
therefore slope of tangent 
Therefore, 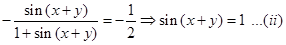
Since 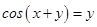 and
and 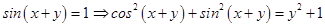
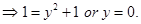
Therefore, 
Therefore, 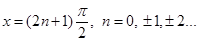
Thus, 
Hence, the points are 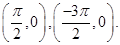
Therefore, equation of tangent at 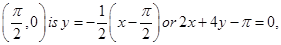 and equation of tangent at
and equation of tangent at  or
or  .
.
13. Find the angle of intersection of the curves  and
and 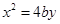 .
.
Sol.Given that 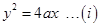 and
and 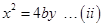 . Solving (i) and (ii), we get
. Solving (i) and (ii), we get

Or 
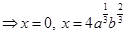
Therefore, the points of intersection are (0, 0) and 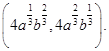
Again, 
Therefore, at (0, 0) the tangent to the curve  is parallel to y-axis and tangent to the curve
is parallel to y-axis and tangent to the curve 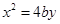 is parallel to x-axis.
is parallel to x-axis.
 Angle between curves
Angle between curves 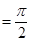
At 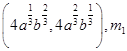 (slope of the tangent to the curve (i))
(slope of the tangent to the curve (i))
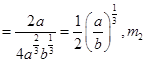 (slope of the tangent to the curve (ii))
(slope of the tangent to the curve (ii)) 
Therefore, 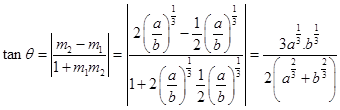
Hence, 
14. Show that the equation of normal at any point on the curve 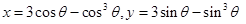 is
is 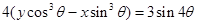 .
.
Sol.We have 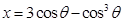
Therefore,

Hence the equation of normal is
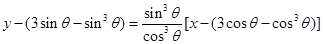
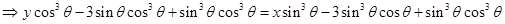
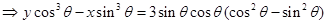
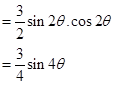
Or 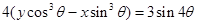
15. Find the maximum and minimum values of
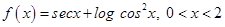
Sol.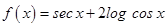
Therefore, 

Therefore, possible values of 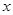 are
are 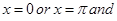
 or
or 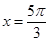
Again, 
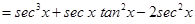
 . We not that
. We not that
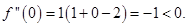 Therefore,
Therefore,  is a point of maxima.
is a point of maxima.
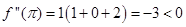 . Therefore,
. Therefore, 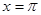 is a point of maxima.
is a point of maxima.
 . Therefore,
. Therefore,  is a point of minima.
is a point of minima.
 . Therefore,
. Therefore, 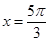 is a point of minima.
is a point of minima.
Maximum Value of y at x = 0 is 1 + 0 = 1
Maximum Value of y at x = 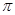 is -1 + 0 = -1
is -1 + 0 = -1
Minimum Value of y at  is
is 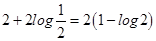
Minimum Value of y at 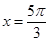 is
is 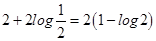
16. Find the area of greatest rectangle that can be inscribed in an ellipse 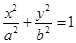
Sol.Let ABCD be the rectangle of maximum area with sides 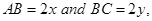 where
where 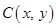 is a point on the ellipse
is a point on the ellipse 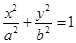 as shown in the Fig. 6.3.
as shown in the Fig. 6.3.

The area A of the rectangle is  which gives
which gives 
Therefore,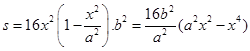
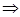

Again, 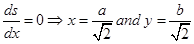
Now, 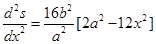
At 
Thus, at  is maximum and hence the area A is maximum.
is maximum and hence the area A is maximum.
Maximum area 
17. Find the difference between the greatest and least values of the function 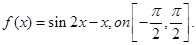
Sol.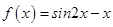

Therefore, 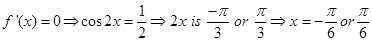
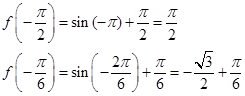

Clearly, 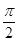 is the greatest value and
is the greatest value and 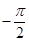 is the least.
is the least.
Therefore, difference 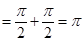
18. An isosceles triangle of vertical angle 2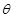 is inscribed in a circle of radius a. Show
is inscribed in a circle of radius a. Show
that the area of triangle is maximum when 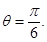
Sol.Let ABC be an isosceles triangle inscribed in the circle with radius a such that AB = AC.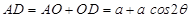 and
and 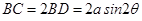 (see fig. 16.4)
(see fig. 16.4)

Therefore, area of the triangle ABC i.e. 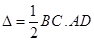
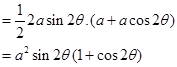
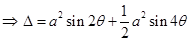
Therefore, 
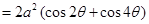
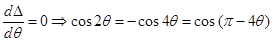
Therefore, 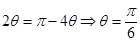
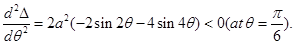
Therefore, Area of triangle is maximum when 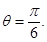
Choose the correct answer from the given four options in each of the following Examples 19 to 23.
19. The abscissa of the point on the curve 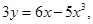 the normal at which passes through origin is:
the normal at which passes through origin is:
(A) 1
(B) 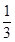
(C) 2
(D) 
Sol.Let 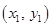 be the point on the given curve
be the point on the given curve  at which the normal passes through the origin. Then we have
at which the normal passes through the origin. Then we have 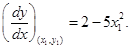 Again the equation of the normal at
Again the equation of the normal at 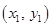 passing through the origin gives
passing through the origin gives 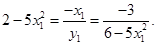
Since  satisfies the equation, therefore, Correct answer is (A).
satisfies the equation, therefore, Correct answer is (A).
20. The two curves 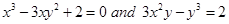
(A) touch each other
(B) cut at right angle
(C) cut at an angle 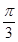
(D) cut at an angle
Sol.From first equation of the curve, we have 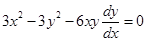
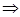
 say and second equation of the curve gives
say and second equation of the curve gives
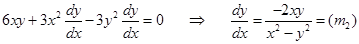 say
say
Since, 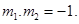 Therefore, correct answer is (B).
Therefore, correct answer is (B).
21. The tangent to the curve given by 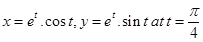 make with x-axis an angle:
make with x-axis an angle:
(A) 0
(B) 
(C) 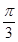
(D) 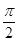
Sol.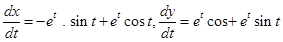
Therefore, 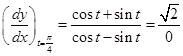 and hence the correct answer is (D).
and hence the correct answer is (D).
22. The equation of the normal to the curve y = sinx at (0, 0) is:
(A) 
(B) 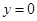
(C) 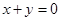
(D) 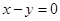
Sol.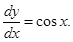 Therefore, slope of normal
Therefore, slope of normal 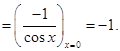 Hence the equation of normal is
Hence the equation of normal is 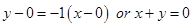
Therefore, correct answer is (C).
23. The point on the curve 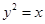 , where the tangent makes an angle of
, where the tangent makes an angle of  with x-axis is
with x-axis is
(A) 
(B) 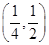
(C) (4, 2)
(D) (1, 1)
Sol.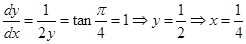
Therefore, correct answer is B.
Fill in the blanks in each of the following Examples 24 to 29.
24. The values of  for which
for which  touches the axis of
touches the axis of 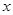 are _______________ .
are _______________ .
Sol.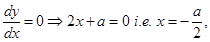
Therefore, 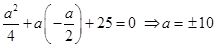
Hence, the values of  are
are 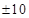
25. If 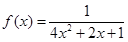 , then its maximum value is _____________.
, then its maximum value is _____________.
Sol.For 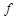 to be maximum,
to be maximum, 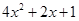 should be minimum i.e.
should be minimum i.e. 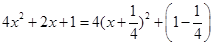 giving the minimum value of
giving the minimum value of  .
.
Hence, maximum value of 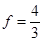 .
.
26. Let 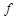 have second derivative at
have second derivative at  such that
such that 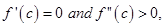 then
then  is a point of __________.
is a point of __________.
Sol.Local minima.
27. Minimum value of 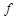 if
if 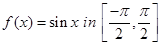 ____________.
____________.
Sol.-1
28. The maximum value of 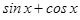 is ____________.
is ____________.
Sol.
29. The rate of change of volume of a sphere with respect to its surface area, when the radius is 2 cm, is ____________.
Sol.