Application of Derivatives - Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper 01
Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives
The instantaneous rate of change at t = 1 for the function f (t) =te-t + 9 is
- 2
- 9
- -1
- -0
The function f (x) = x2, for all real x, is
- Neither decreasing nor increasing
- Increasing
- Decreasing
- None of these
The slope of the tangent to the curve x = a sint, y = a at the point ‘t’ is
- none of these
- tan t
- cot t
The function f (x) = x2 - 2x is strict decreasing in the interval
- none of these
- R
The equation of the tangent to the curve y2 = 4ax at the point (at2, 2at) is
- ty = x + at2
- none of these
- tx + y =at3
- ty = x - at2
- The maximum value of is ________.
- The minimum value of f if f(x) = sin x in [] is ________.
- The equation of normal to the curve y = tan x at (0, 0) is ________.
Find the approximate value of f(3.02) where f(x) = 3x2 + 5x + 3.
If the line ax+by+c=0 is a normal to the curve xy=1,then show that either a>0,b<0 or a<0,b>0
Find the interval in which the function f(x) = x2e-x is increasing.
The volume of a sphere is increasing at the rate of 3 cubic centimeter per second. Find the rate of increase of its surface area, when the radius is 2 cm.
Find the approximate value of .
Show that the function f(x) = 4x3 - 18x2 + 27x - 7 is always increasing on R.
Show that the height of the cylinder of maximum volume that can be inscribed in a sphere of radius a is .
A particle moves along the curve 6y = x3 + 2. Find the points on the curve at which the y-coordinate is changing 8 times as fast as the x – coordinate.
Find the equation of tangent to the curve at the point, where it cuts the X-axis.
Show that semi – vertical angle of right circular cone of given surface area and maximum volume is .
CBSE Test Paper 01
Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives
Solution
- (d) 0, Explanation:
- (a) Neither decreasing nor increasing, Explanation: f(x) = x2
f'(x) = 2x for all x in R.
Since f ‘(x) = 2x > 0 for x >0, and f ‘ (x) = 2x< 0 for x < 0, therefore on R, f is neither increasing nor decreasing. Infact , f is strict increasing on [ 0, ) and strict decreasing on (- ]. - (d) cot t, Explanation: Given,
Slope of the tangent - (d) , Explanation: f ‘ (x ) = 2x – 2 = 2 ( x - 1) <0 if x < 1 i.e. x . Hence f is strict decreasing in
- (a) ty = x +at2, Explanation:
at is
Slope of tangent
Hence, equation of tangent is - -1
- x + y = 0
Put
f(3.02)={3(9)+5(3)+3}+{6(3)+5}×0.02 =45+0.46
f(3.02) = 45.46- we have, xy =1
The slope of the normal = x2
If ax+by+c=0 is normal to the curve xy=1,then - f(x) = x2e-x
Differentiating w.r.t x, we get,
f'(x) =
For increasing function, f'(x)
[ is always positive]
[ since - ( x - 2) will change the inequality )
Here x < 0 & (x - 2) > 0 x < 0 & x > 2 0 < x < 2
But when x > 0 & (x - 2) < 0 x > 0 & x < 2 - Let r be the radius of sphere and V be its volume.
Then V = ........(i)
Given, = 3 cm3/s
Differentiating (i) both sides w.r.t x,we get,
.......(ii)
Now, let S be the surface area of sphere, then S =
[using Eq.(ii)]
when r = 2, then = 3 cm2/s
Therefore,the rate of inrcrease of the surface area of sphere is 3 cm/s when it's radius is 2 cm - Let x = 2
and
let y = x5
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get
Now,
= 32 - 0.080 = 31.920 - Here, f(x) =4x3 - 18x2 + 27x - 7
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get
f'(x) = 12x2 - 36x + 27
f'(x) = 3(4x2 -12 + 9)
f'(x) = 3(x - 3)2
f'(x) 0
Since, a perfect square number cannot be negative]
Given function f(x) is an increasing function on R. 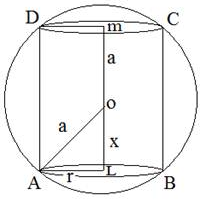
For maximum/minimum
= - tive maximum
Volume is maximum at
Height of cylinder of maximum volume is
= 2x- Given curve is 6y = x3 + 2 ...(i)
so,
Put the value of x in equation (1)
When x = 4
6y = ( 4 )3 + 2
6y = 64 + 2
6y = 66
So, point is (4, 11)
Now, When x = - 4
6y = ( - 4}3 + 2
= - 64 + 2
So the point is - Given equation of curve is
.......(i)
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get
[dividing numerator and denominator by x2 - 5x + 6]
Also, given that curve cuts X-axis, so its y-coordinate is zero.
Put y = 0 in Eq. (i), we get
x= 7
So, curve passes through the point (7, 0).
Now, slope of tangent at (7,0) is
Hence, the required equation of tangent passing through the point (7, 0) having slope 1/20 is
y - 0 = (x - 7)
20y = x - 7
x - 20y = 7 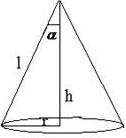
(given)
Let v be the volume
Now
Now
= + ve
Hence minimum
Now
We have
3 r = l