Vector Algebra - Exemplar Solutions
CBSE Class–12 Mathematics
NCERT Exemplar
Chapter - 10
Vector Algebra - Short Answer Questions
1. Find the unit vector in the direction of the sum of the vectors 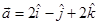 and
and 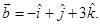
Sol. Let 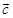 denote the sum of
denote the sum of 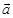 and
and 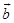 . We have
. We have
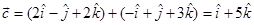
Now 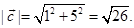
Thus, the required unit vector is 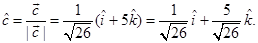
2. Find a vector of magnitude 11 in the direction opposite to that of 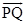 , where
, where 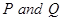 are the points
are the points 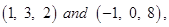 respectively.
respectively.
Sol. The vector with initial point 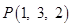 and terminal point
and terminal point 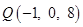 is given by
is given by
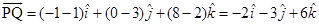
Thus, 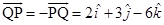
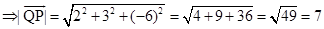
Therefore, unit vector in the direction of 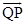 is given by
is given by
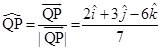
Hence, the required vector of magnitude 11 in direction of 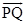 is
is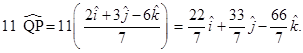
3. Find the position vector of a point R which divides the line joining the two points P and Q with position vectors 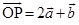 and
and 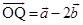 , respectively, in the ratio
, respectively, in the ratio  , (i) internally and (ii) externally.
, (i) internally and (ii) externally.
Sol. (i) The position vector of the point R dividing the join of P and Q internally in the ratio 1:2 is given by
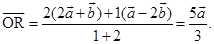
(ii) The position vector of the point R’ dividing the join of P and Q in the ratio  externally is given by
externally is given by
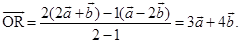
4. If the points 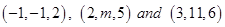 are collinear, find the value of
are collinear, find the value of 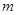 .
.
Sol. Let the given points be 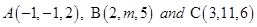 . Then
. Then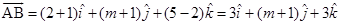
And 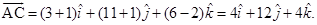
Since 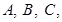 are collinear, we have
are collinear, we have 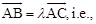
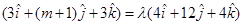
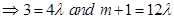 (solving equations)
(solving equations)
Therefore, 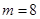 .
.
5. Find a vector 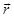 of magnitude
of magnitude 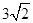 units which makes an angle of
units which makes an angle of 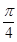 and
and 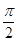 with
with 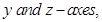 respectively.
respectively.
Sol. Here 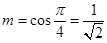 and
and 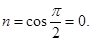
Therefore, 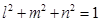 gives
gives
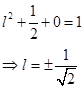
Hence, the required vector 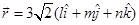 is given by
is given by
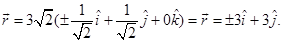
6. If 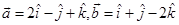 and
and 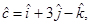 find
find 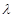 such that
such that 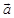 is perpendicular to
is perpendicular to 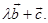
Sol. We have
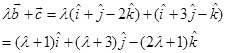
Since 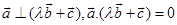
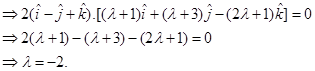
7. Find all vectors of magnitude 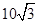 that are perpendicular to the plane of
that are perpendicular to the plane of 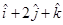 and
and 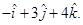
Sol. Let 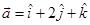 and
and 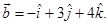 Then
Then
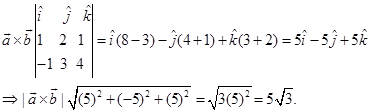
Therefore, unit vector perpendicular to the plane of 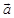 and
and 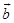 is given by
is given by
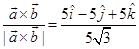
Hence, vectors of magnitude of 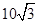 that are perpendicular to plane of
that are perpendicular to plane of 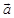 and
and 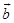 are
are 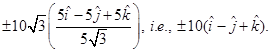
8. Using vectors, prove that 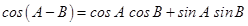 .
.
Sol. Let 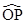 and
and 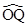 be unit vectors making angles A and B, respectively, with positive direction of
be unit vectors making angles A and B, respectively, with positive direction of 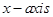 . Then
. Then 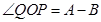 [Fig. 10.1]
[Fig. 10.1]
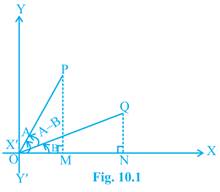
We know 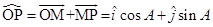 and
and 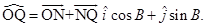
By definition 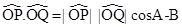
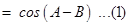
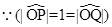
In terms of components, we have
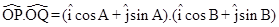
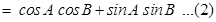
From (1) and (2), we get
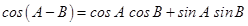 .
.
9. Prove that in a 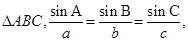 where
where 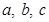 represents the magnitude of the sides opposite to vertices
represents the magnitude of the sides opposite to vertices 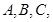 respectively.
respectively.
Sol. Let the three sides of the triangle BC, CA and AB be represented by 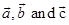 , respectively [Fig. 10.2]
, respectively [Fig. 10.2]
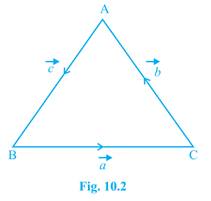
We have 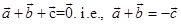
Which pre-cross multiplying by 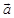 , and post cross multiplying by
, and post cross multiplying by 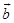 , gives
, gives
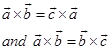
respectively. Therefore,
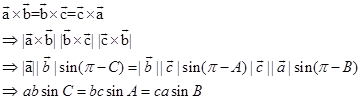
Dividing by abc, we get
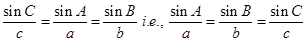
Choose the correct answer from the given the four options in each of the Examples 10 to 21.
10. The magnitude of the vector 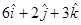 is
is
(A) 5
(B) 7
(C) 12
(D) 1
Sol. (B) is the correct answer.
11 The position vector of the point which divides the join of points with position vectors 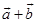 and
and 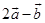 in the ratio 1: 2 is
in the ratio 1: 2 is
(A) 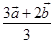
(B) 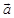
(C) 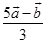
(D) 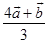
Sol. (D) is the correct answer. Applying section formula, the position vector of the required point is 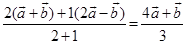
12. The vector with initial point 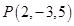 and terminal point
and terminal point 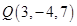 is
is
(A) 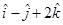
(B) 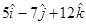
(C) 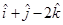
(D) None of these
Sol. (A) is the correct answer.
13. The angle between the vectors 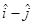 and
and 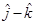 is
is
(A) 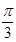
(B) 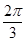
(C) 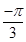
(D) 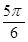
Sol. (B) is the correct answer. Apply in formula 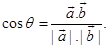
14. The value of 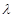 for which the two vectors
for which the two vectors 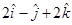 and
and 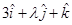 are perpendicular is
are perpendicular is
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 6
(D) 8
Sol. (D) is the correct answer.
15. The area of the parallelogram whose adjacent sides are 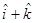 and
and 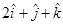 is
is
(A) 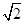
(B) 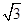
(C) 3
(D) 4
Sol. (B) is the correct answer. Area of the parallelogram whose adjacent sides are 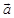 and
and 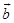 is
is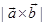 .
.
16. If 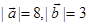 and
and 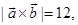 then value of
then value of 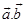 is
is
(A) 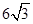
(B) 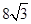
(C) 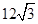
(D) None of these
Sol. (C) is the correct answer. Using the formula 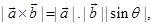 we get
we get 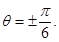
Therefore, 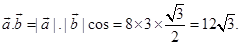
17. The 2 vectors 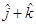 and
and 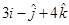 represents the two sides AB and AC, respectively of a
represents the two sides AB and AC, respectively of a  . The length of the Median through A is
. The length of the Median through A is
(A) 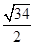
(B) 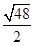
(C) 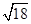
(D) None of these
Sol. (A) is the correct answer. Median 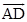 is given by
is given by
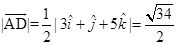
18. The projection of vector 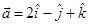 along
along 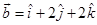 is
is
(A) 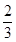
(B) 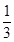
(C) 2
(D) 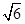
Sol. (A) is the correct answer. Projection of a vector 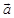 on
on 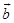 is
is
19. If 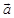 and
and 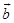 are unit vector, then what is the angle between
are unit vector, then what is the angle between 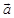 and
and 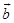 for
for 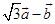 be a unit vector?
be a unit vector?
(A) 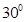
(B) 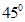
(C) 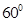
(D) 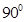
Sol. (A) is the correct answer. We have
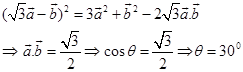
20. The unit vector perpendicular to the vectors 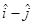 and
and 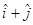 forming a right-handed system is
forming a right-handed system is
(A) 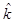
(B) 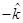
(C) 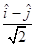
(D) 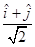
Sol. (A) is the correct answer. Required unit vector is 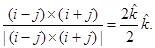
21. If 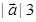 and
and 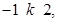 then
then 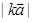 lies in the interval
lies in the interval
(A) 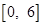
(B) 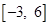
(C) 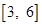
(D) 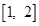
Sol. (A) is the correct answer. The smallest value of 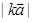 will exist at numerically smallest value of k, i.e., at k = 0, which gives
will exist at numerically smallest value of k, i.e., at k = 0, which gives 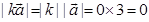
The numerically greatest value of 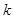 is 2 at which
is 2 at which